Anti aging Treatments in Ware Hertfordshire
Anti aging treatments at Beauty Bar in Ware Hertfordshire
Treatments for aging skin in Ware
Anti-aging treatments are highly effective procedures that significantly thicken, revitalise, and tighten the skin. They are design for men and women of all ages (over 18) as corrective or preventative treatments.
Many people by the age of 30 begin to notice the first signs of aging when they look in the mirror. Many women are not happy with how their skin looks. Aging is a gradual process and lifestyle, UV radiation, and the environment in which we live often don’t support our skin’s health.
To prevent and slow down the aging process, we recommended to have some non-invasive cosmetic treatments that would be chosen to meet the individual needs of your skin. The therapy protects the skin, corrects signs of aging, and plumps up and thickens the skin through collagen induction. Depending on your age and the condition of your skin, we can select the appropriate products and treatments just for you.

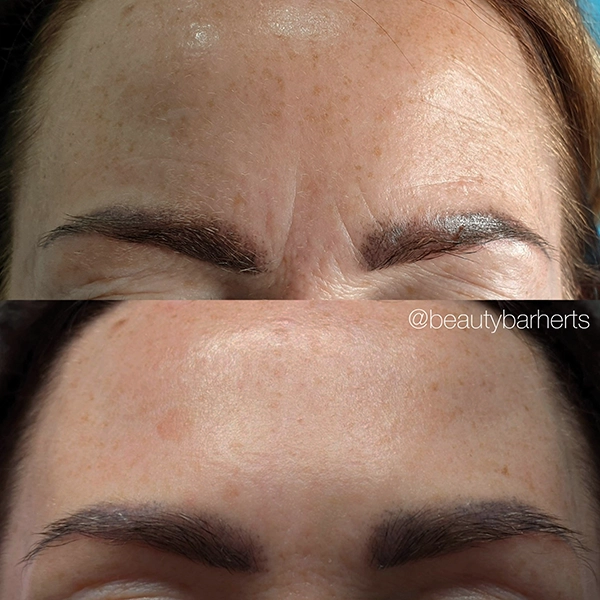
Treatment Focus Areas
Anti aging treatments focus on addressing the most common aging problems. This could be volume loss, skin plumping and collagen boosting, wrinkle reduction, age spot reduction and improvement of the skin texture. From the age of 30, skin requires more hydration, stimulation of fibroblasts, collagen, and elastin is important. Due to collagen increase, wrinkles become less visible, skin gets plumper and thicker.
Depending on the cause of the signs of aging we may recommend different products and treatments. If for example, your problem lies in the lack of volume in the mid face, treating your skin may not give you the results you were hoping for. During the consultation we will assess the problem areas and recommend appropriate treatment to effectively manage it.
Why Fibroblasts are so important in the aging process
Fibroblasts, are often referred to as the architects of the skin, and play a very important role in maintaining its structure, elasticity, and health.
Fibroblasts – The Skin’s Master of Construction
Fibroblasts are cells found in the connective tissue of the skin, responsible for the production of collagen, elastin, and other extracellular matrix proteins. They are involved in maintaining the skin’s structure, texture, and health.
Fibroblasts are central to collagen and elastin synthesis. They play a role in the production and secretion of both proteins, which maintain skin elasticity, firmness, and a youthful look. Fibroblasts also regulate the turnover and remodelling of collagen and elastin fibers.
Changes in fibroblast activity is linked to the aging process. As we age, fibroblast activity declines, leading to decreased collagen and elastin production. This contributes to fine lines, wrinkles, sagging skin, and a loss of skin elasticity. Stimulating fibroblasts through treatments like microneedling, Rf needling, chemical peels, skin boosters, mesotherapy and RF can help counteract these effects and promote a youthful look for longer.

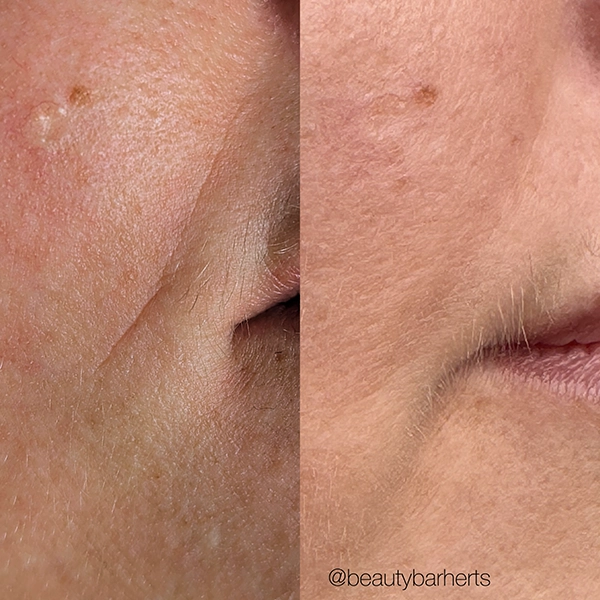
Anti aging treatments at Beauty Bar in Ware
Microneedling
Microneedling is a minimally invasive treatment that involves creating controlled micro-injuries in the skin using fine needles. These micro-injuries stimulate the skin’s natural healing response, triggering fibroblast activation. Activated fibroblasts release growth factors and initiate collagen synthesis, leading to improved skin texture, reduced scars, wrinkles, and rejuvenation.
Radiofrequency (RF)
RF treatments use electromagnetic waves to deliver controlled heat energy into the skin. The heat generated by RF promotes collagen remodelling and stimulates fibroblast activity. This process leads to the production of new collagen fibers and the tightening of existing collagen, resulting in improved skin tone, texture, and firmness.
Collagen and Elastin Remodelling
Microneedling, RF, chemical peels, skin boosters and fractional RF treatments work by inducing controlled damage to the skin, triggering a healing response that involves fibroblasts. Fibroblasts not only produce new collagen and elastin fibers but also participate in the remodelling of existing fibers. This remodelling process helps improve the strength, organisation, and quality of collagen and elastin in the skin.
Science Behind Collagen-Boosting Aesthetic Treatments
Collagen maintains strength, elasticity, and young look of our skin.
Collagen boosting treatments are renowned for rejuvenating the skin and addressing signs of aging. Maintaining regular treatments and completing the recommended course is important for achieving their benefits.
Collagen-boosting aesthetic treatments work by stimulating the body’s natural collagen synthesis process. By triggering controlled injury or heat, these treatments stimulate the skin’s healing response, leading to increased collagen production. Regular treatments give continuous stimulation of collagen and cumulative benefits.
These treatments aren’t showing immediate results. Collagen synthesis is a complex process that takes time. After an aesthetic treatment, the body initiates various biochemical events to repair and rebuild the treated area. It takes several weeks for fibroblast cells in the skin to produce new collagen and for existing collagen fibers to remodel. This remodelling process is important for achieving long-lasting results.
Regular treatment intervals keep collagen production at high levels. By following the recommended timeframe, you are making sure that fibroblasts continuously receive signals to produce collagen. Consistent collagen activation encourages a consistent production and remodelling of collagen fibers, leading to optimal results.
Collagen production and remodelling occur gradually over time. Noticeable changes in skin texture, elasticity, and overall look develop over a series of treatments. Each session builds upon the previous one, allowing for progressive collagen enhancement.
When too long of a gap is left between collagen boosting treatments, the natural progression of collagen can be hindered. Without regular stimulation, collagen activity decrease, and collagen fibers revert to their previous state. Regular treatments prevent regression, allowing collagen production to progress steadily and sustainably.
It’s important to complete a full course of collagen boosting treatments for full benefits.
Collagen synthesis has various stages – initiation, proliferation, and remodelling. By completing a course of treatments we address each stage adequately.
Factors such as age, health, lifestyle habits, skin damage and environmental factors can affect the collagen production and the final results.
What causes skin to age?
- Natural aging that occurs over time due to genetic factors and chronological aging.
- Aging caused by external factors in the environment, like tanning.
- Unhealthy lifestyle habits. Smoking and drinking alcohol. Poor nutrition, inadequate hydration, lack of exercise, and chronic stress.
- Air pollution
- Hormonal changes during menopause
- Repeated facial expressions, such as frowning or squinting.
What tanning does to your skin?
The sun emits different types of UV radiation, primarily UVA and UVB.
UVA rays penetrate deep, damaging collagen and elastin fibers. UVB rays affect the outer layers and cause sunburns. Both generate free radicals that contribute to oxidative stress and cellular damage.
Tanning breaks down collagen resulting in wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.
Tanning also affects elastin, the fibers become damaged, causing the skin to lose its ability to bounce back, wrinkles, sagging, and leathery texture.
Tanning leads to localised increase or irregular distribution of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour. This results in the age spots, freckles, and other hyperpigmentation issues.
Tanning causes direct damage to the DNA in skin cells. This leads to mutations and genetic abnormalities. The body’s natural defense mechanisms against these DNA damages become less efficient with age, leading to potential skin cancers.
Genetics and skin aging
Studies have identified specific genes that regulate the production of collagen, elastin, and other structural proteins in the skin. Genetics can affect the rate at which these proteins are produced, leading to differences in skin elasticity, firmness, wrinkles and fine lines.
Genetic factors can influence the body’s response to inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which contribute to skin aging. Genes involved in immune responses, antioxidant defence, and DNA repair mechanisms can affect the skin’s ability to combat and repair damage caused by inflammation and oxidative stress.
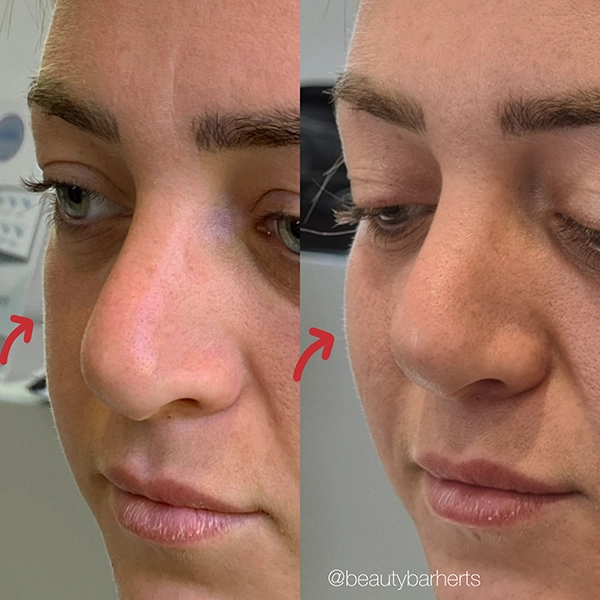
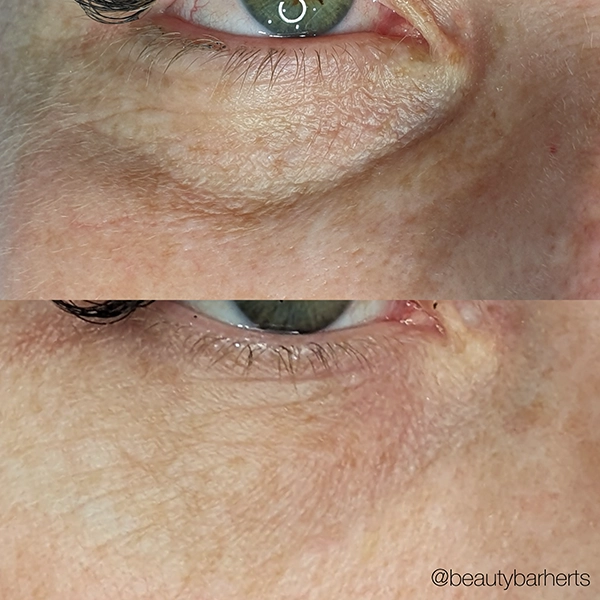
Common signs of aging skin
- Fine lines and wrinkles are caused decreased collagen production, loss of skin elasticity, and repetitive facial expressions over time.
- As we age, the supportive tissues in our skin, such as collagen and elastin fibers, gradually weaken. This can lead to sagging skin, particularly in areas such as the cheeks, jawline, and neck.
- Aging skin gets drier and rougher due to a decline in natural oil production and a decrease in the skin’s ability to retain moisture.
- Over time, accumulated tanning causes uneven distribution of melanin, resulting inmage spots, freckles, and other pigmentation irregularities.
- With age skin becomes thinner due to less collagen and elastin fibers. Thinner skin is more prone to damage and can appear translucent or fragile.
- The skin’s ability to regenerate and repair itself slows down, leading to a more uneven skin tone and a rougher texture. This can make the skin look less vibrant and smooth.
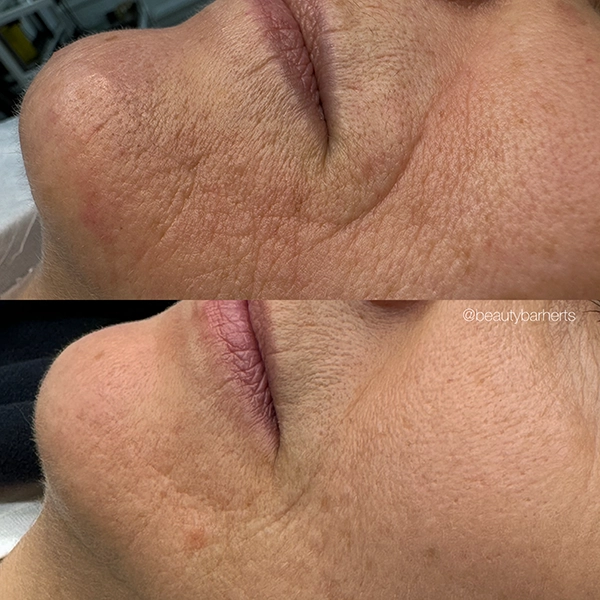
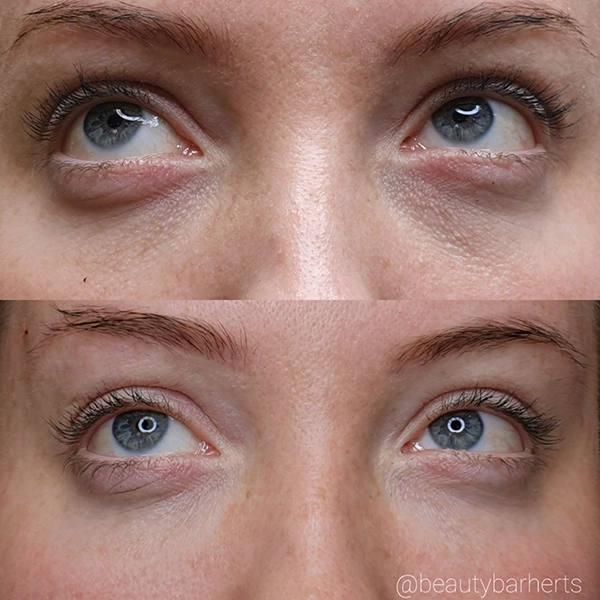
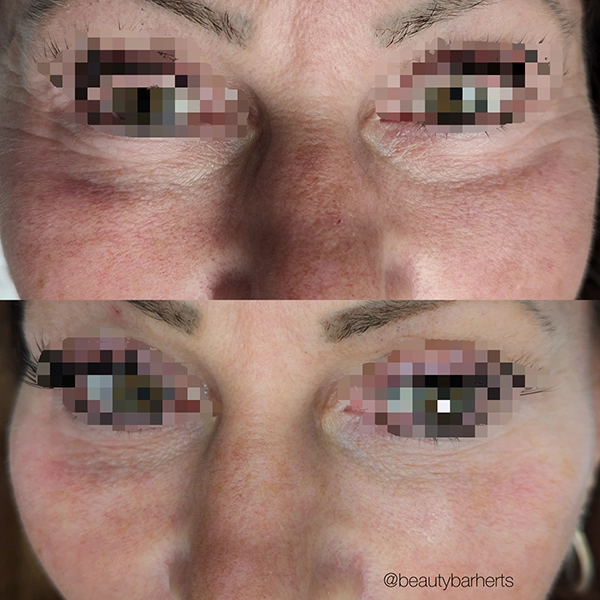
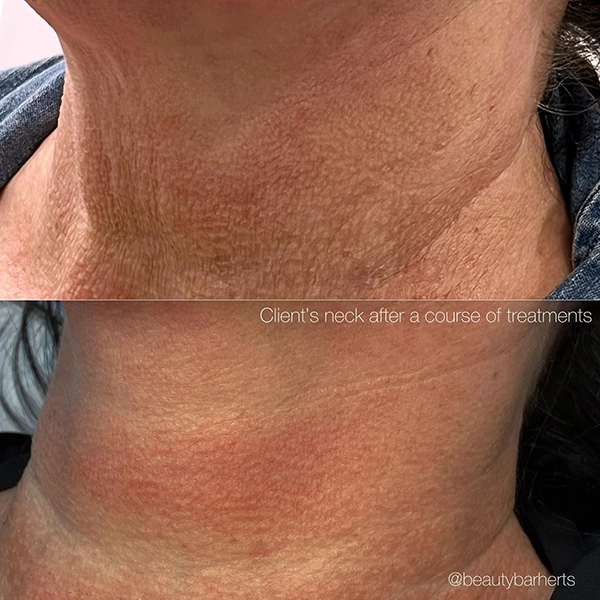
What professional salon treatments in Ware Hertfordshire can address aging skin?
Retinoids are derived from vitamin A. They have been proven effective in reducing fine lines, wrinkles, and improving skin texture.
Chemical peels like Biorepeel Cl3 promote the growth of new, healthier skin cells. They can reduce fine lines, wrinkles, and uneven pigmentation, also boost collagen.
Dermal fillers are used to restore volume, smooth fine lines and wrinkles, and lift facial contours.
Wrinkle reduction treatments relax muscles. It helps reduce the look of dynamic wrinkles caused by muscle contractions, such as crow’s feet, frown and forehead lines.
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy stimulates the production of collagen and elastin, and results in improved skin texture, diminished fine lines, and a younger looking skin.
Profhilo is a skin booster that provides deep hydration to the skin and boost collagen and elastin. It improves skin quality, gives a natural glow, and plumps up the skin.
Skin boosters are treatments containing hyaluronic acid or polinucleotides, and result in the intense hydration, collagen production, improving skin texture, and elasticity.
RF Needling, also known as fractional radiofrequency (RF) microneedling stimulates collagen production, tightens the skin, and improves overall skin texture. It helps to firm and tighten the skin while promoting a youthful and rejuvenated look.
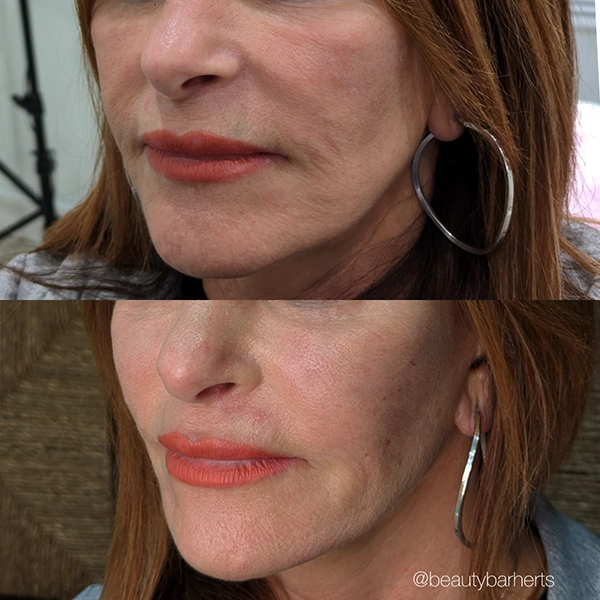
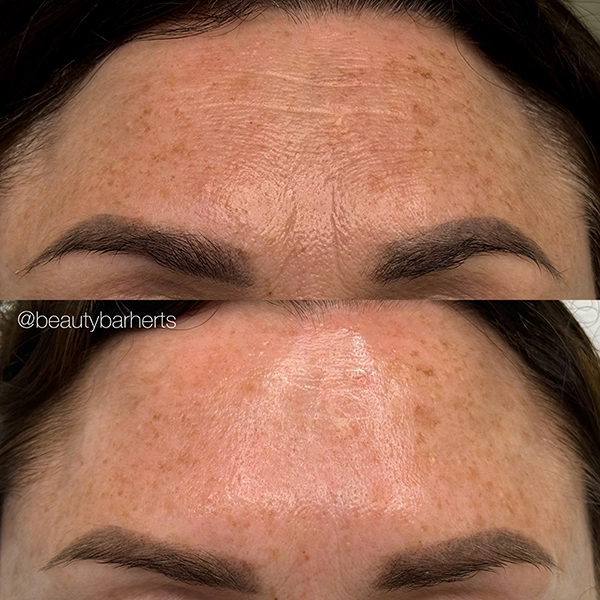


Book your anti aging appointment at Beauty Bar in Ware Hertfordshire
Rejuvenating anti-aging treatments at Beauty Bar in Ware, Hertfordshire. Restore youthful radiance with our expert services. We welcome clients from the nearby towns like Hertford, Hoddesdon, Broxbourne, Stevenage, Hatfield, Welwyn Garden City and Cheshunt. Book your appointment today!
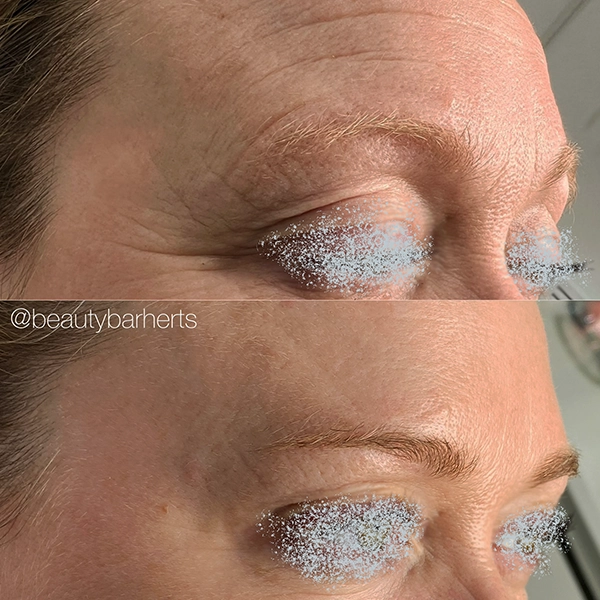

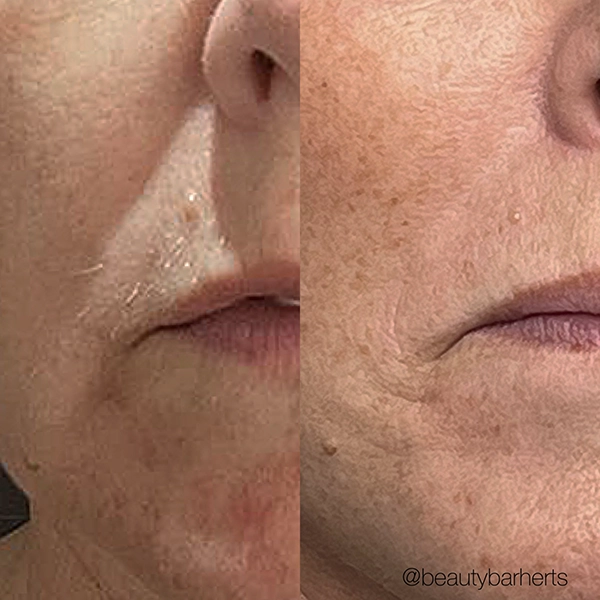
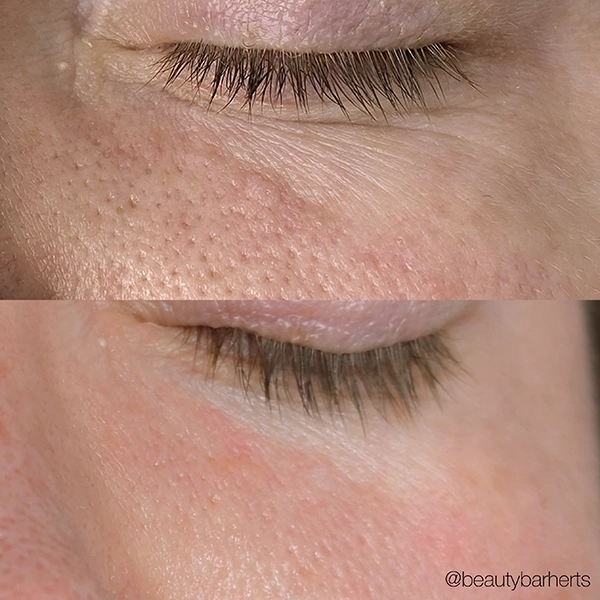
Book your Anti aging treatments in Ware Hertfordshire
Skin anti age Treatments at Beauty Bar in Ware
Contact us today and take your first step to a better skin by booking your anti aging treatment.
